본 자료는 edwith 최성준님이 강의하신 Bayesian Deep Learning 강의를 참고하였다.
핵심 키워드
Probability
공정한 주사위 게임을 예로 들어보자.
이제부터

여기서 우리는 measure를 probability 로 아직 받아들이면 안된다. probability는 sample space에서 정의된 면적이다 라고만 받아들여야 한다.
- The ramdon experiment should be well defined.
- outcomes : 나올 수 있는 모든 관측된 sample space에서 어떤 것이 정해진 후 나오는 값
- sample point
- sample space
Definition ( probability )
1.
2.
3. For disjoint sets
4.
그렇다면 위 axioms을 만족하는 probability 를 어떻게 만들 수 있을까?
Probability allocation function
Recall that probability
아래에 보이는 검은색 선은 sample space에 들어가 있고, 그때의 면적을 측정하면 probability가 된다.

conditional probability of A given B

Chain rule
-
-
total probability law:
Bayes' rule
When
prior probability가 주어지고 posterior probability를 찾는 것이 bayesian이라고 할 수 있다.
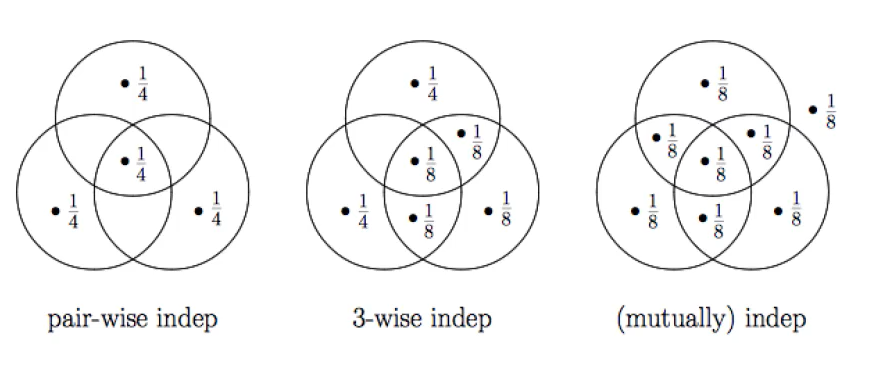
independent events
independet event를 번역 그대로 관계없는 독립적인 사건이라고 보는 것이 아니라,
independent
'Mathematics > Statistics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Bayesian] Bayesian Deep Learning - Random Process (0) | 2021.07.12 |
|---|---|
| [Bayesian] Bayesian Deep Learning - Random variable (0) | 2021.07.09 |
| [Bayesian] Bayesian Deep Learning - Measure theory (0) | 2021.07.06 |
| [Bayesian] Bayesian Deep Learning - Set theory (0) | 2021.07.06 |
| [Statisctics] Maximum Likelihood Estimate (0) | 2021.06.29 |